What Are Lab Tubes?
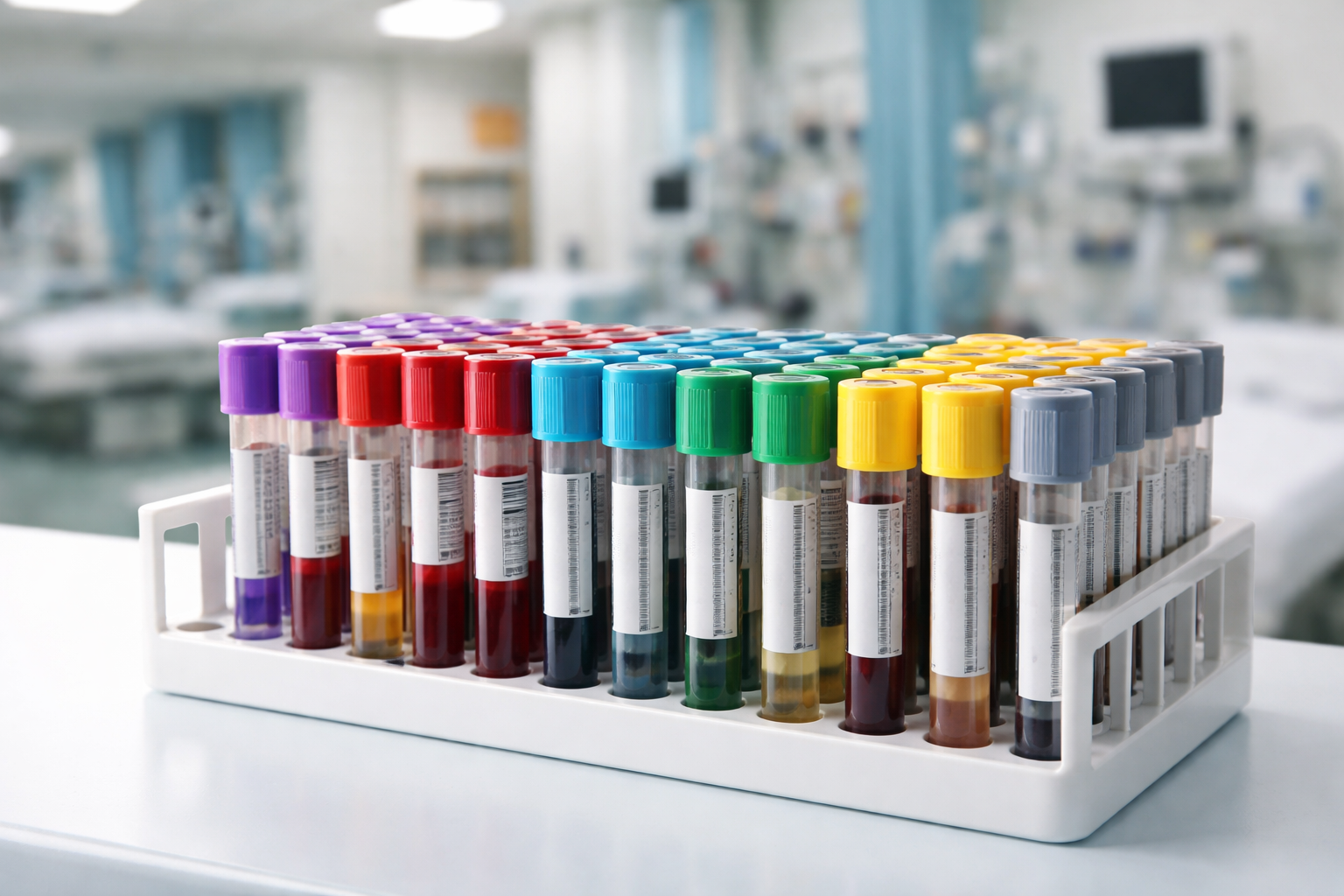
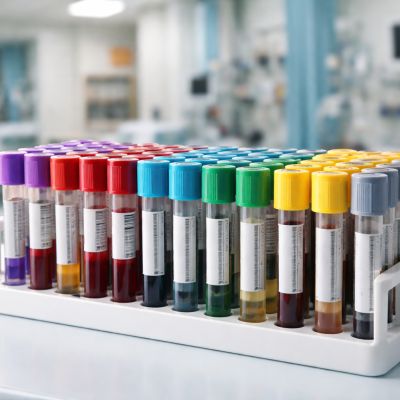
Medical lab tubes, also known as specimen collection tubes, are small cylindrical containers made of glass or plastic that collect and store biological samples (such as blood, urine, or saliva) for laboratory analysis. These tubes usually have a vacuum seal and a colored cap that shows whether there are any additives in the tube. Each tube has a specific use, and the color, size, and chemical additive of the tube determine what type of test it serves. Lab tubes may seem very simple, but they preserve the sample and ensure that the test is done correctly by design.
Why Are Medical Lab Tubes Important?
Lab tubes play a very important role in obtaining accurate and reliable test results. Engineers have designed these tubes to preserve the sample, prevent contamination, and maintain consistency. Almost all blood tests, from routine to specialized tests (such as genetic or hormone tests), require the right tube to collect and transport the sample. Without these tubes, laboratory testing would be a messy and unreliable process, and the risk of errors and misdiagnosis would be very high.
Types of Lab Tubes (By Color)
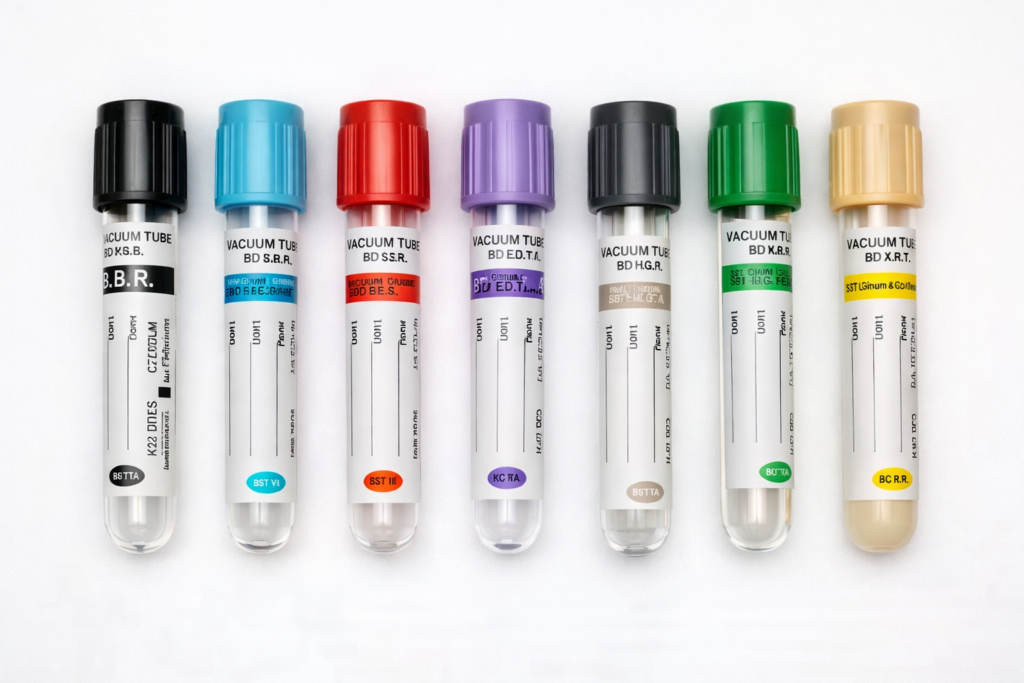
The tubes used in the lab have various colored caps. Each cap color represents a certain type of additive or lack thereof and its application. All manufacturers have standardized their color-coding systems. It is vital that you only use the right tube for the right test. If you don’t do that, you might make your sample unusable for that test. Below are some of the commonly used lab tubes and their additives and application:
-
Red-Top Tube (No Additive)
This tube has no additives. When blood is put into a red-top tube, it clots and allows for serum separation for further testing. Red-top tubes are used for blood typing and other tests that require serum. (Additives: No additives)
-
Gold-Top Tube (Serum Separator Tube)
The gold-top tube has additives such as a clot activator and a gel. When blood is put into a gold-top tube and then spun in a centrifuge, the blood clots and then separates from the serum by the gel. This tube is used for tests that require serum for blood chemistry, metabolic panels, thyroid function tests, and lipid profiles. (Additives: Clot activator and Gel)
-
Light Blue-Top Tube (Sodium Citrate)
The blue-top tube contains sodium citrate as an anticoagulant. Clinicians use blue-top tubes for coagulation studies, which include blood clotting tests such as prothrombin time (PT), activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT), and international normalized ratio (INR). The sodium citrate anticoagulant works by binding to the calcium ions present in the blood, which otherwise would cause the blood to coagulate. This enables the blood specialists to test the blood for its coagulating ability. (Additives: Sodium citrate)
-
Green-Top Tube (Heparin)
The green-top tube contains heparin as an anticoagulant. Laboratories use green-top tubes for testing blood plasma rather than serum. This is because the heparin anticoagulant prevents the blood from coagulating or forming clots. This anticoagulant works by preventing the formation of thrombin, which otherwise would cause the blood to coagulate. This enables the blood specialists to test the blood for its chemistry, such as the levels of sodium, cholesterol, and blood gases.
-
Yellow-Top Tube (ACD or SPS)
“Yellow top” tubes contain two different anticoagulants:
-
- Tubes containing SPS (Sodium Polyanethol Sulfonate) – These tubes are used for blood culture tests because SPS maintains microbes alive for culture tests by inhibiting clotting and complement activation.
- Tubes containing ACD (Acid Citrate Dextrose) – These tubes are used for collecting cells for DNA tests or tissue typing because ACD maintains cell viability.These tubes are usually sterile. (Additives: SPS or ACD solution)
-
Lavender/Purple-Top Tube (EDTA)
Purple-top tubes contain EDTA (Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid), which inhibits clotting by binding to calcium. EDTA tubes are the preferred choice for hematology tests. For instance, EDTA tubes can be used for a complete blood count (CBC), blood smear tests, HbA1c tests, and other blood cell tests. EDTA maintains the form and shape of blood cells, so accurate results can be ensured. (Additives: EDTA)
-
Grey-Top Tube (Fluoride/Oxalate)
The grey-top tube generally consists of sodium fluoride and potassium oxalate as additives. Sodium fluoride is used as a preservative. It stops the glucose from being used by cells. This tube is used for blood tests such as blood sugar levels and diagnosing diabetes and lactic acid levels. In short, the grey tube maintains the sugar levels in the blood sample from decreasing before they are used for testing. Additives: Sodium fluoride and sometimes potassium oxalate
-
Black-Top Tube (Sodium Citrate for ESR)
The black-top tube consists of sodium citrate as an additive. In addition, it is used for the erythrocyte sedimentation rate blood test. The laboratory uses this tube for measuring how fast red blood cells are settling in the blood. This helps in detecting inflammation. In short, the black-top tube is similar to the blue tube that consists of sodium citrate. Additives: Sodium citrate
-
Pink-Top Tube (EDTA)
The pink-top tube consists of EDTA as an additive. It is used for blood bank procedures. The pink tube is used by hospitals for blood typing and crossmatching. In short, it is used for blood transfusions. Additives: EDTA
How to Properly Handle Lab Tubes

There are several ways in which lab tubes should be handled and stored, and below are a few important tips:
- Label Tubes Clearly: Ensure that you label the lab tube clearly, especially the patient’s name and the date when the sample was collected. This helps the lab identify the sample and avoid mix-ups.
- Use the Right Tube for the Test: Be sure to use the right type of tube for the test you are conducting. This is important because, for example, a CBC test should not be conducted using a plain red top tube, as the results may be inaccurate.
- Store Samples Properly: After collecting the sample, ensure you store it properly, as some blood samples may need to be refrigerated, while others should be left at room temperature, depending on the test’s requirements.
- Avoid Contamination: Make sure that the tube and sample are not contaminated with external materials. For example, when taking samples, handle them aseptically and do not touch the opening of the tube with your fingers. Even minute amounts of contaminants can influence the outcome of the test.
- Follow the Right Order of Draw: When multiple tubes are being drawn in a single session, the tubes should be filled in the right order (order of draw) to prevent cross-contamination of additives. For example, blood culture tubes are drawn first, followed by citrate tubes (blue), then serum tubes, and so on.
FAQ
-
Can I reuse lab tubes?
No. Lab tubes are single-use only. It is important to use a new tube for each sample to avoid contamination and ensure accurate results. Reusing a tube may result in contamination of the new sample with leftover additives or pathogens, which may result in incorrect results and pose health hazards.
-
What is an EDTA tube used for?
An EDTA tube, which has a purple or pink cap, is mainly used for hematology studies. It is the regular tube for a complete blood count (CBC) and other studies where the whole blood needs to be analyzed. The EDTA in the tube prevents clot formation and preserves the blood cells for analysis.
-
Why is EDTA used for CBC?
EDTA is used for CBC because it prevents the blood from clotting and preserves the morphology of blood cells for accurate counting and analysis. In short, EDTA maintains the blood sample in its natural state so that the automatic counters and microscopes can function properly.
-
Does EDTA remove calcium?
Yes. EDTA is a chelating agent that sequesters (removes) calcium ions in the blood sample by binding them. Calcium ions are needed for blood clotting. Therefore, by removing calcium ions, EDTA prevents blood from clotting in the tube. This is the exact reason why EDTA is such a good anticoagulant for blood tests.